Products
Built multiple sets of modular, multi-functional intelligent drug automatic synthesis platform
18F-JR1004 material
Keywords: synthetic equipment disposable consumables
Classification:
Tracers

Hotline:
18F-JR1004 material
Graphic Details
18F-JR1004 Materials
1. Drug Name (Generic Name, Chemical Name, English Name, Pinyin, and rationale for custom names if any)
Generic Name: 18F-JR1004
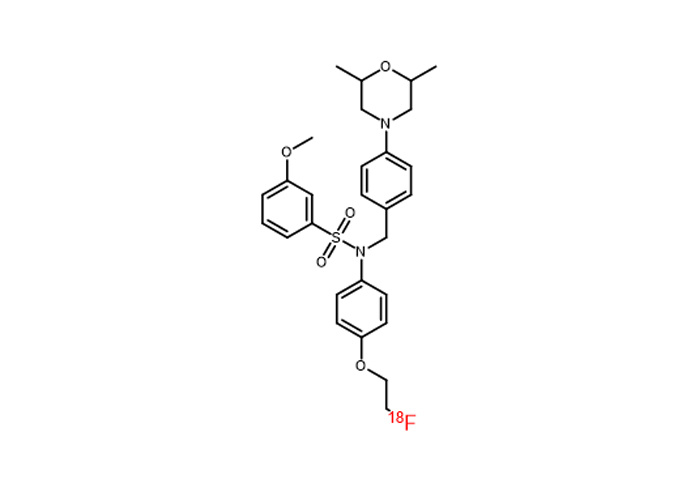
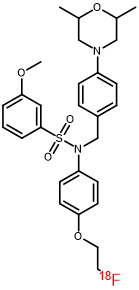
Chemical Name: N-[4-( diethylamino ) benzyl ]-N-[4-(2-( fluoro -18F) ethoxy ) phenyl ]-3,5- dimethoxyaniline
English Name: N-(4-(diethylamino)benzyl)-N-(4-(2-(fluoro-18F)ethoxy)phenyl)-3,5-dimethoxyaniline
Pinyin: 18F-JR1004
2. Chemical Structure, Molecular Weight, Molecular Formula
Chemical Structure:
3. Rationale ( Literature on the research and application of this product at home and abroad )
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is the most common subtype of pancreatic cancer, accounting for over 90% of all pancreatic cancer cases. Due to its insidious early symptoms, lack of effective screening methods, and highly invasive biological characteristics, PDAC is usually diagnosed at a late stage, resulting in a 5-year survival rate of less than 10%. Traditional diagnostic methods, such as imaging examinations (CT, MRI, etc.) and tumor marker detection (CA19-9, etc.), can assist in diagnosis to some extent, but they still have limitations in early detection and accurate assessment of tumors. Therefore, the development of molecular imaging techniques capable of achieving early diagnosis and accurate staging is of great significance for improving the prognosis of PDAC patients. In recent years, the rapid development of molecular imaging technology has provided new tools for the precise diagnosis and treatment monitoring of tumors. Positron emission tomography (PET) is an advanced medical imaging technique that allows us to see activity within the body in a unique way. PET imaging technology, with its high sensitivity, functional imaging, whole-body scanning, high resolution, quantitative analysis, non-invasiveness, multimodal imaging, and wide clinical applications, has become an indispensable diagnostic and research tool in modern medicine. It can not only detect and accurately diagnose diseases early but also provide important basis for the development of treatment plans and efficacy evaluation.
The cannabinoid type 2 receptor (CB2R), as a member of the G protein-coupled receptor family, is significantly upregulated in various tumors, including PDAC. Studies have shown that CB2R plays an important role in the occurrence, development, and metastasis of PDAC and may be a potential diagnostic and therapeutic target.
The development of CB2R-based PET probes provides a new direction for molecular imaging of PDAC. By specifically binding to CB2R, these probes can sensitively detect the biological behavior of tumors in vivo, providing important information for the early diagnosis, staging, treatment response assessment, and prognosis prediction of PDAC. In addition, CB2R-targeted PET imaging may also provide a basis for personalized treatment of PDAC, such as screening patients suitable for cannabinoid therapy by assessing the expression level of CB2R. The author aims to explore the biological role of CB2R in PDAC and its potential as a molecular imaging target, and to review the application prospects of CB2R-based PET probes in the diagnosis and treatment of PDAC, in order to provide new ideas and strategies for the precision medicine of PDAC.
4 Research methods, experimental conditions, etc., for imaging or simulated clinical functional determination tests of target organs and the whole body of experimental animals, and imaging or functional determination results at various time phases of observation
I. Whole-body and delayed imaging of experimental animals
1. Materials and Methods
1.1 Experimental Animals
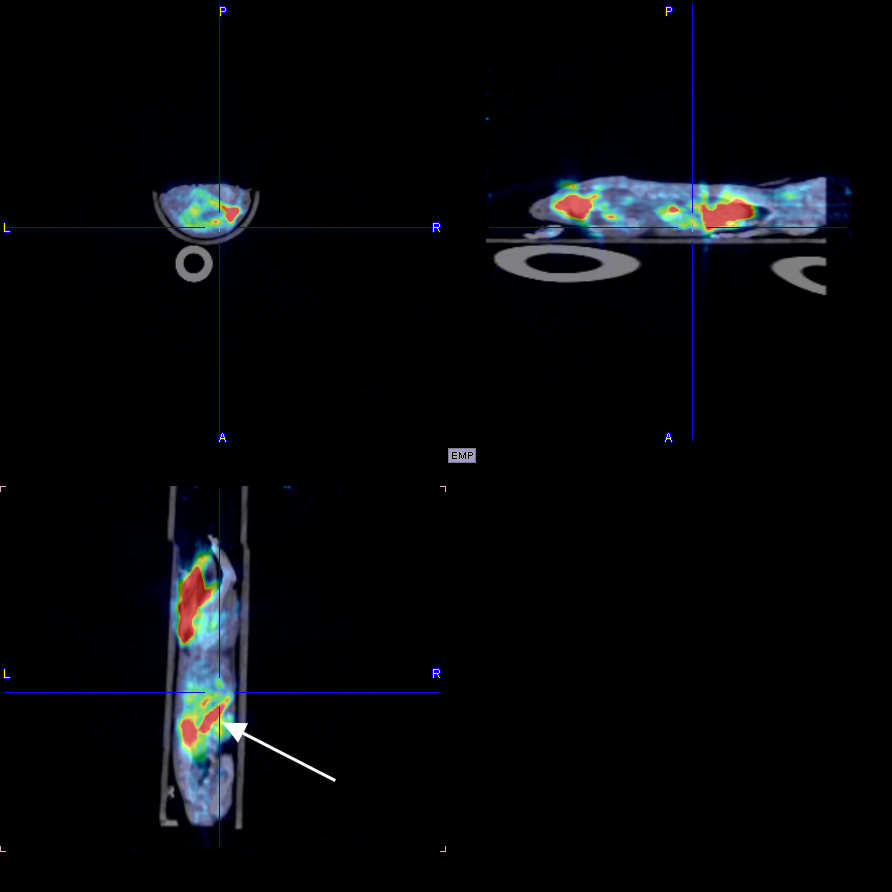
The experimental animals were 2 mice, weighing approximately 25g, male, obtained from the Zhejiang University laboratory. Images were collected at multiple time points after drug injection to obtain a map of drug distribution in the body. After imaging, the experimental animals gradually woke up and recovered normally, with good diet, defecation, and mental state.
The following is a 30min imaging image
5. Drug Instructions
Generic Name: 18F-JR1004
Chemical Name:
N-[4-(diethylamino)benzyl]-N-[4-(2-(fluoro-18F)ethoxy)phenyl]-3,5-dimethoxyaniline
English Name:
N-(4-(diethylamino)benzyl)-N-(4-(2-(fluoro-18F)ethoxy)phenyl)-3,5-dimethoxyaniline
Pinyin:
18F-JR1004
[Properties]
This product is a colorless, clear or slightly yellow, clear solution.
[Indications]
18F-JR1004 is used for tumor diagnosis and staging assessment, cardiovascular disease imaging, and monitoring of bone lesions or bone metastases, etc.
[18F-JR1004 PET/CT Brain Imaging Procedure]
Pre-examination preparation
Fasting requirements: Subjects need to fast for 4-6 hours (water is allowed) to avoid blood glucose fluctuations interfering with the distribution of the imaging agent.
Blood glucose monitoring: Blood glucose needs to be checked before injection, usually requiring control to ≤11mmol/L.
Contraindicated adjustments: Suspend medications that may interfere with the results (such as insulin, hormone medications), and avoid strenuous exercise.
Imaging agent injection and resting period
Intravenous injection: The 18F-JR1004 tracer is administered intravenously, with the dose adjusted according to body weight and examination purpose.
Resting period: After injection, rest in a quiet, dark environment for 45-60 minutes, avoiding activity or mental stimulation during this period to ensure the specific distribution of the tracer in the brain tissue.
Brain imaging scan
Positioning: The patient lies supine on the scanning bed, with the head fixed using a dedicated headrest, maintaining steady breathing and a still body.
CT Scan: A low-dose CT scan (approximately 10 minutes) is performed first to obtain anatomical images of the brain.
PET Scan: This is followed by a PET scan (approximately 20-30 minutes) to detect the metabolic distribution and targeted binding of 18F-JR1004.
Image Processing and Diagnosis
Data Fusion: The PET functional images and CT anatomical images are fused using software to generate a three-dimensional brain metabolic image.
Clinical Interpretation: A nuclear medicine physician, considering metabolic activity, lesion location, and patient history, issues a diagnostic report.
Post-Examination Precautions
Radiation Protection: It is recommended to drink plenty of water and urinate frequently after the examination to accelerate the excretion of the radioactive tracer.
Result Acquisition: The formal report is usually available within 1-2 working days.
Follow-up Arrangements: Brain imaging with 18F-JR1004 and 18F-FDG should be spaced at least 10 half-lives (or 20 hours) apart.
This product can only be used in medical institutions with a "Radioactive Pharmaceutical Use License".
[Adverse Reactions]
None have been found.
[Contraindications]
None have been found.
[Precautions]
If discoloration or cloudiness occurs, discontinue use.
This product can only be used in medical institutions with a "Radioactive Pharmaceutical Use License".
[Use in Pregnant and Lactating Women]
Contraindicated in pregnant and lactating women.
[Pediatric Use]
Reduce the dose appropriately according to body weight.
[Specifications]
0.37~7.40GBq.
[Storage and Packaging]
This product is sealed in a 30ml vial and placed in a lead container.
[Expiration Date]
Calculated from the calibration time as 6 hours.
[Manufacturer]
Name: Hangzhou Jirei Technology Co., Ltd.
Address: No. 319, Shenjia Road, Gongshu District, Hangzhou, Fengqi Valley Yunzhang Industrial Park
Postal Code: 234122
Telephone Number: 0571-87701916
Previous Page
18F-JR1002 material
Next Page
Related Products
Consulting